Wound Care: Carrageenan as a Hydrocolloid
Hydrocolloids in Wound Care
The wound care industry is already familiar with the term ‘hydrocolloid’, but it's essential to distinguish what constitutes a hydrocolloid from a manufacturer's perspective compared to an end user's perspective.
In chemistry, hydrocolloids are defined as water-soluble macromolecules that, when in solution, form a gel-like matrix, which affects the rheological properties. Examples for hydrocolloids are: Alginate, carrageenan, dextran, chitosan, hyaluronic acid and many more (1). These polymers are utilized in wound dressings such as hydrogel patches or fiber dressings, where they support the wound healing through coating, moisturizing, filling or covering.

Carrageenan – What is it?
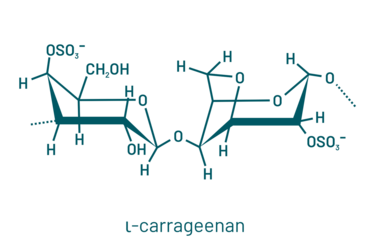
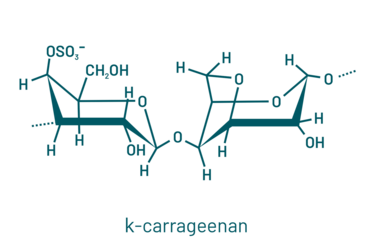
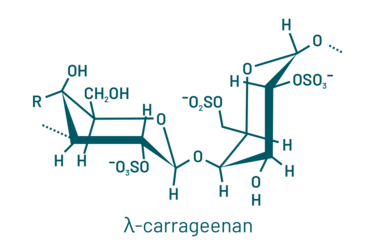
Carrageenans are sulfated polysaccharides present in the cell walls of red algae (2). They are obtained from different species like Gigartina spp. or Chondrus Chrispus and are harvested under different conditions, like hand harvesting in cold Chilean waters to cultivation in hot Asian waters. These seaweeds undergo alkali processing to yield nearly pure fractions with distinct chemical compositions, resulting in three primary polysaccharide types: Iota, kappa, and lambda.
Iota carrageenans are sulfated at carbon-2 (unlike kappa) while lambda carrageenans are highly sulfated and lack 3,6-anhydro galactose. Commercially available carrageenan products typically range in molecular weight from 100 to 1000 kDa (3).
Coming from this chemical structure, carrageenans are able to jellify. Kappa and iota form a 3D double helical network as the sulfate groups are facing the exterior of the spiral chains and may crosslink. Lambda carrageenan’s sulfate groups face the interior, hence crosslinking is prevented.
Widely known from the food industry for applications like custard, milk-based desserts or even water jellies, carrageenans also play a vital role in wound dressing development.
Carrageenan in Wound Care Application
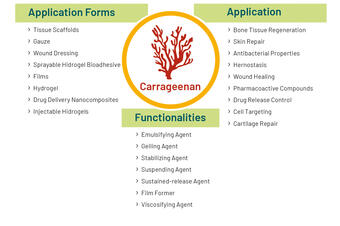
In wound care formulations carrageenans serve as stabilizer, binder, disintegrator, solubilizer, thickener and coating agent. They are cumulative with other ingredients and are often used in drug delivery system utilizing heat reversible gelation, ionic crosslinking and modification of the main chain (2).
- Encapsulation (2)
Carrageenan enables the encapsulation of actives, reducing gastrointestinal disorders by delivering anti-inflammatory agents. Beads can also mask aftertaste and prolong release of the active ingredients into the body. The pH sensitivity facilitates controlled release in the intestines, and its heat-gelling property simplifies bead formation, even with oily contents.
- Films (2)
In film applications, carrageenan is often co-formulated with other ingredients. It enhances the mechanical resistance of the film preparation and provides significant mucoadhesive properties. The resulting films protect the wound and absorb exudate while ensuring stability and a clean wound milieu with the encapsulation antimicrobial agents.
- Hydrogel (2)
In hydrogel dressings, carrageenan functions as matrix forming polymer. Due to its hydrophilic nature and easy crosslink-ability it provides stability and a high absorption capacity. The wound dressing further benefits from the antiadhesive properties and very good biocompatibility.
- Nanofibers via Electrospinning (3)
The beneficial properties of carrageenan can also be used in fibrous formulations. In electrospinning, its addition to for example PVA based formulations results in fibers with antibacterial effects and good biocompatibility.
Conclusion
Carrageenans offer a comprehensive set of biological, chemical and physical benefits to a variety of different wound care applications. Especially their antibacterial properties as well as the gelling property and rheological behavior make it an excellent matrix material and enhancer for biomedical products.
Are you Interested in exploring carrageenan's potential? We warmly invite you to connect with us. Let us discuss how carrageenan can benefit your product.

References
(1) LL Loyd, Carbohydrate polymers as wound management aid (1998), Carbohydrate polymers 1998,37 , 315-322
(2) Edisson-Mauricio Pacheco-Quito, Carrageenan : Drug delivery systems and other biomedical applications (2020), Marine Drugs 2020, 18, 583, p
(3) Bogdan Neamtu, Carrageenan-Based Compounds as Wound Healing Materials (2022), International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022,23,9117, p









